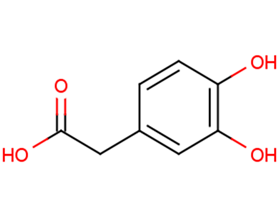
34-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
CAS No. 102-32-9
34-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid( 34-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid | 34-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid | DOPAC )
Catalog No. M19538 CAS No. 102-32-9
34-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid is the main neuronal metabolite of dopamine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name34-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description34-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid is the main neuronal metabolite of dopamine.
-
Description34-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid is the main neuronal metabolite of dopamine.
-
In Vitro3,4-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid is the main neuronal metabolite of dopamine. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 3,4-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid (DOPAC) is derived from intra-neuronal metabolism of cytoplasmic dopamine, and acts as a sensitive and specific biomarker of central dopamine deficiency.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms34-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid | 34-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid | DOPAC
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number102-32-9
-
Formula Weight168.15
-
Molecular FormulaC8H8O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM;Water: 10 mg/mL
-
SMILESOC(=O)Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Goldstein DS et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid ratios of cysteinyl-dopamine/34-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in parkinsonian synucleinopathies. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Oct;31:79-86.
molnova catalog



related products
-
7α,25-Dihydroxychole...
7α, 25-dihydroxycholesterol (7α,25-OHC) is a potent and selective agonist and endogenous ligand of the orphan GPCR receptor EBI2 (GPR183). 7α, 25-dihydroxycholesterol can serve as a chemokine directing migration of B cells, T cells and dendritic cells[1][2], and it is highly potent at activating EBI2 (EC50=140 pM; Kd=450 pM).
-
Uridine diphosphate ...
Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid ammonium (UDP-α-D-glucuronic acid ammonium) is a precursor of many plant cell wall polysaccharides and is required for the production of seed mucilage.
-
Estrone sulfate pota...
Estrone sulfate potassium is an estrogen ester and conjugate, a natural endogenous steroid.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


